How To Reduce Your Risk Of Breast Cancer - Dietitians' Viewpoint
Article Date: 02 Oct 2011
In the USA breast cancer incidence is the highest in the world, at 128.6 cases per 100,000 Caucasian women, and 112.6 per 100,000 African Americans. In the UK breast cancer is the most prevalent type of cancer, and women over 50 years are at the highest risk. Each year in the UK approximately 47,000 women are diagnosed with the disease and around 341 men.
Breast cancer rates have increased and it is believed that nutritional and lifestyle factors, such as excessive alcohol consumption, diets high in fat, diets low in fiber, and obesity play a part in breast cancer risk, although no clear connection has been compellingly demonstrated.
Nutrigenomics is a new scientific field that combines genetics and nutrition in order to identify how the food we eat, or bioactive food molecules affect our genes. It is suggested that eating foods that have a nutrigenomic effect will cause certain genes to switch on or off.
Nutrigenomics is the study of how various foods interact with particular genes to raise the risk of chronic diseases, such as heart disease, come cancers, obesity, and diabetes type 2. It also strives to find out at molecular level how common chemicals in our diet affect our health by changing gene expression and the structure of a human's genome. The principle behind nutrigenomics is that the impact of diet on health depends on a person's genetic makeup.
Mariëtte Abrahams, a spokesperson for Freelance Dietitians and registered nutritionist, explained:
"With a strong trend and demand for prevention and self-care, we are on the brink of a new era. In the future, we may be able to provide more personalized dietary advice to individuals who have inherited gene variants that increases their risk of developing breast cancer.
Previous studies have indicated that women carrying specific genetic variants of the breast cancer gene may be more responsive to the cancer-reducing effect of catechins in green tea and genistein in soya, but there is still a lot of work that needs to be done."
Early diagnosis of breast cancer, if it does occur, is vital for treatment to be effective. People can considerably lower their risk of developing breast cancer by following a healthy diet and adopting a healthy lifestyle, which should also include physical activity and at least 7 to 8 hours good quality sleep every night.
Nutritionist play a key role in helping individuals lead a healthy lifestyle and balanced diet. Dietitians can recommend food choices prior to being diagnosed, during diagnosis or after.
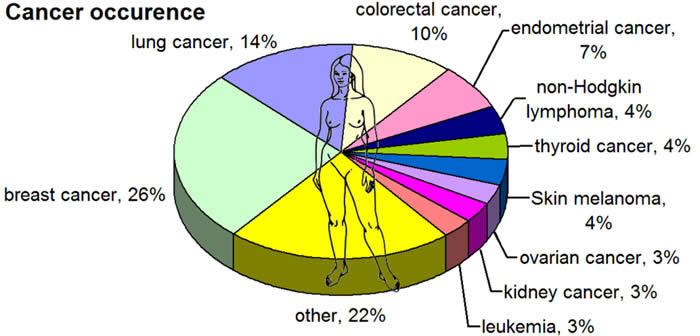
These data refer to the USA only
How to reduce your risk of developing breast cancer
Bodyweight control - make sure you do regular physical exercise, and choose healthy foods, such as fruits and vegetables, wholegrains, nuts, and dairy products low in fat. For women a health body mass index (BMI) ranges from 18.5 to 25. Even though BMI is a helpful tool to assess body status, it is not the only indicator. BMI can be calculated by using your weight in kilograms (kg) and height in meters (m), with the formula BMI = weight/height.
Eat more vegetarian foods - eat more fruits and vegetables, the fiber (lignins) in them as well as isoflavones from legumes, soya, and beans, have been linked to a reduced risk of developing the disease. Try to eat at least 5 portions daily. Visit the British Dietetic Association for simple ways to incorporate more fruits and vegetables into your diet.
Lower your intake of saturated fat - avoid eating saturated fats (from animal products), instead replace them with poly and monounsaturated fats 'good fats', which are found in avocados, olive oil, nuts, and salmon.
Reduce Salt and sugar intake - lower your salt intake by staying clear of foods that are picked, cured or processed, as well as not adding extra salt to your meal. Avoid consuming cakes, pastries, and biscuits as they contain refined sugars.
Watch your alcohol consumption - women who consume too much alcohol regularly have a higher risk of developing breast cancer, previous studies have shown. To lower your risk stick to the recommended daily intake of 2-3 units per day, or 14 units per week. One unit is the same to ½ a standard glass of wine (175ml).
Other factors can also reduce breast cancer risk, such as breastfeeding, consuming adequate amounts of vitamin D, and not smoking.
It is important that a woman does not miss her breast cancer screenings.
Some women may consider prophylactic (preventive) bilateral mastectomy if they carry the BRCA1 and BRCA2 (genetic) mutations. Patients are advised to discuss their optioins extensively with their doctor and/or a genetic counselor.
Written by Grace Rattue
Copyright: Medical News Today